What Is Electrotherapy?
Electrotherapy is the use of electrical energy as a medical treatment. In medicine, the term electrotherapy can apply to a variety of treatments, including the use of electrical devices such as deep brain stimulators for neurological disease. The term has also been applied specifically to the use of electric current to speed wound healing. Additionally, the term "electrotherapy" or "electromagnetic therapy" has also been applied to a range of alternative medical devices and treatments.(
Source)
Electrotherapy in Physiotherapy
In physiotherapy, we do use some effective electrotherapy modalities to treat range of conditions such as muscle pain,soft tissue injury, muscle weakness, nerve damage and so on. The modalities we use has been clinically proven to be effective to treat such conditions. Common Modalities used in Malaysian hospitals include:-
- Hotpack,coldpack- (yes,they are included in electrotherapy because the machines which manipulates temperature,which is knows as the freezer and hydrocollator,uses electricity to function)
- Ultrasound therapy machine(abbreaviated as US)
- IFT (interferential therapy) machine
- SWD (shortwave diathermy) machine
- TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation)
- Infrared therapy
- UV therapy
- Traction machine
- Laser therapy
So lets learn more about the modalities:-
Hotpack
-its basically a pack made out of thick cloth filled with wheat,flaxseed,buckwheat or any other material which can absorb heat and release it slowly over a period of time. The pack is dropped in a machine called hydrocollator which is filled with water and a heating element heats up the water. Over a period of time,the hotpack is heated up. To apply on a patient, the pack is lifted from the machine,wrapped in certain layer of towels and placed on the problem area. The hot pack gives moist heat to the area applied.
Hotpacks are helpful in reducing muscle and soft tissue pain,relaxing muscles and help in soft tissue healing.Conditions which can benefit from hotpack include
-joint pain
-muscle tightness
-back pain
-chronic cases of pain
-muscle and ligament injury
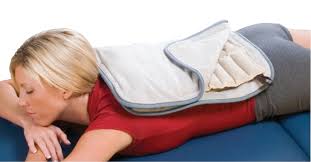 |
the light brown pack is known as the hotpack.
And a typical apperance of patient having hotpack
for the back |
Coldpack
-An ice pack or cold pack is a plastic sac of ice, refrigerant gel or liquid. The refrigerant, usually non-toxic, can absorb a considerable amount of heat. It is commonly used as a cold compress to alleviate the pain of minor injuries. The packs are simply placed in a freezer. To use,its wrapped in a wet towel and placed on the problem area.
Coldpacks is used to treat mostly fresh sport injuries. The cold helps by shrinking your blood vessels and slowing blood flow to the area and stopping the formation of swelling and internal bleeding. And cold also helps hide the sensation of pain from reaching the human brain,effectively relieving pain.
 |
| Typical Icepack. needs to be frozen in the freezer before use |
Ultrasound Therapy machine
-Ultrasound is applied using a transducer or applicator that is in direct contact with the patient's skin. Gel is used on all surfaces of the head to reduce friction and assist transmission of the ultrasonic waves. Therapeutic ultrasound in physical therapy is alternating compression and rarefaction of sound waves with a frequency of >20,000 cycles/second.
Ultrasound therapy benefits by speeding up of the healing process from the increase in blood flow in the treated area. The second is the decrease in pain from the reduction of swelling and edema. The third is the gentle massage of muscles tendons and/ or ligaments in the treated area because no strain is added and any scar tissue is softened.
Conditions which ultrasound may be used for treatment include the follow examples: Ligament Sprains, Muscle Strains, Tendonitis, Joint Inflammation, Plantar fasciitis, Metatarsalgia, Facet Irritation, Impingement syndrome, Bursitis, Rheumatoid arthritis, Osteoarthritis, and Scar Tissue Adhesion.
 |
| Ultrasound therapy |
IFT (interferential therapy) machine
-uses a mid-frequency electrical signal to treat muscular spasms and strains. The current produces a massaging effect over the affected area at periodic intervals, and this stimulates the secretion of endorphins, the body's natural pain relievers, thus relaxing strained muscles and promoting soft-tissue healing. Its use is contraindicated if the affected area has wounds, cuts or infections. It helps relieve pain,stimulate muscles,increase local blood flow, and reduce edema.
 |
| Interferential Therapy machine |
SWD machine
Short wave diathermy machines utilize two condenser plates that are placed on either side of the body part to be treated. Another mode of application is by induction coils that are pliable and can be molded to fit the part of the body under treatment. As the high-frequency waves travel through the body tissues between the condensers or the coils, they are converted into heat. The degree of heat and depth of penetration depend in part on the absorptive and resistance properties of the tissues that the waves encounter.
Useful for ,Inflammation of Shoulder Joint,Inflammation of Elbow Joint (Tennis Elbow),Degeneration of Joints of Neck (Cervical Spondylosis),Degeneration of Joints like knee and Hip (Osteoarthritis),Ligament Sprains in knee Joint,Low Back Ache,Plantar Fascitis (Heel Pain).
But currently its being phased out in foreign countries due to risk of side effects of the wave.
 |
| Shortwave diathermy machine |
 |
Patient with TENS fixed on the
upper back |
TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation)
the use of electric current produced by a device to stimulate the nerves for therapeutic purposes. TENS by definition covers the complete range of transcutaneously applied currents used for nerve excitation although the term is often used with a more restrictive intent, namely to describe the kind of pulses produced by portable stimulators used to treat pain. The unit is usually connected to the skin using two or more electrodes. A typical battery-operated TENS unit is able to modulate pulse width, frequency and intensity. It can be set either to stimulate muscle contraction, or to give pain relieve.The machine's compact size makes it ideal to be brought along with the patient.
Infrared therapy
Infrared radiation is a convenient system to heat parts of our body. It has the advantage over direct contact in that radiation can heat directly the area where the blood capillaries and neuron terminals are. When heat comes from a direct contact source it has to heat the external layer of the skin, and heat is transferred to the deeper layer by conduction. Since
heat conduction needs a temperature gradient to proceed, and there is a maximum temperature that can be safely used (around 42°C), this means lower temperature where warming is needed.It is an alternative to hotpacks.
 |
| infrared light |
Mechanical Traction
Mechanical traction are tables that the patient lies down on, either on their back or face down, depending on which therapy the doctor decides would be most beneficial for their condition. There are a few different types of traction tables.
For patients suffering from low back pain, there is Lumbar Traction, which is designed to specifically target the lumbar curve(lower spine), restoring your lumbar spine to it's appropriate degree of curvature. Cervical Traction is designed for the cervical curve (neck spine), helping to reduce neck tension and is especially beneficial for headache sufferers. Each of these machines has rollers that are brought up under your back, helping to reduce tension, break up scar tissue, hydrate discs, and bring new blood and fluids to the area, helping your body to heal faster.
 |
| patient undergoing lower back traction |
Well,that ends this post. Maybe this article was too technical to understand. But its enough if you can know the names of the machines. You might come across similar looking machines if you visit physiotherapy centre. At least you will recognise the machine and have some idea about it. Technical wise, just leave it to the professional. See you againYatta!!












